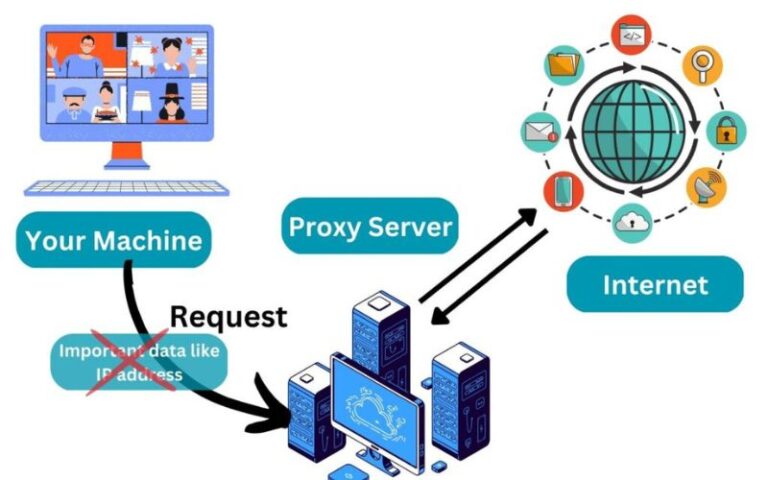
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet, routing your online traffic through its own servers. This can provide a range of benefits, from enhanced security and privacy to improved performance and bypassing content restrictions. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the different types of proxy servers, walk you through the setup process on various operating systems, and discuss best practices for using a proxy server for anonymous browsing.
Why Use a Proxy Server?
Proxy servers offer several compelling reasons for users to consider setting one up:
- Privacy and Security: By routing your internet traffic through a proxy server, you can conceal your IP address and protect your online activities from prying eyes, making it harder for websites or third parties to track your browsing history and personal information.
- Bypass Restrictions: Proxy servers can be used to circumvent content restrictions and access websites or online services that may be blocked in your region, workplace, or school.
- Improved Performance: Proxy servers can cache frequently accessed web content, reducing the time it takes to load pages and improving overall browsing speed, especially for users with slower internet connections.
- Anonymity: Proxy servers can help you browse the web anonymously, making it more difficult for websites to identify you and track your online activities.
- Parental Controls: Proxy servers can be used to filter and restrict access to certain websites, providing a layer of protection for children or employees in a corporate environment.
Different Types of Proxy Servers
There are several types of proxy servers, each with its own unique features and use cases:
- Web Proxy: A web proxy is the most common type of proxy server, providing a simple way to access websites and online content through a third-party server.
- Transparent Proxy: A transparent proxy is a proxy server that is invisible to the client, meaning the client is unaware that their traffic is being routed through the proxy.
- Anonymous Proxy: An anonymous proxy server hides the user’s IP address, providing a higher level of privacy and anonymity compared to a standard web proxy.
- Reverse Proxy: A reverse proxy server sits between the client and the web server, acting as an intermediary and providing additional features such as load balancing, caching, and security.
- SOCKS Proxy: SOCKS proxies operate at the network layer, allowing them to handle a wider range of protocols beyond just HTTP/HTTPS, making them more versatile than web proxies.
Setting Up a Proxy Server on Windows
- Open the Settings app and navigate to the “Network & Internet” section.
- Click on “Proxy” and toggle the “Use a proxy server” option to “On.”
- Enter the proxy server address and port number provided by your proxy service.
- (Optional) Configure the “Bypass your proxy server for these addresses” field to exclude specific websites or domains from using the proxy.
- Click “Save” to apply the proxy settings.
Setting Up a Proxy Server on macOS
- Open the System Preferences and click on the “Network” icon.
- Select the network interface you want to configure (e.g., Wi-Fi or Ethernet) and click the “Advanced” button.
- Navigate to the “Proxies” tab and select the appropriate proxy type (e.g., “Web Proxy (HTTP)” or “Secure Web Proxy (HTTPS)”).
- Enter the proxy server address and port number provided by your proxy service.
- (Optional) Configure the “Bypass proxy settings for these Hosts & Domains” field to exclude specific websites or domains from using the proxy.
- Click “OK” to save the changes and then click “Apply” to apply the proxy settings
Setting Up a Proxy Server on Linux
- Open the system settings and navigate to the “Network” or “Network Connections” section.
- Select the network interface you want to configure and click the “Edit” or “Properties” button.
- Navigate to the “IPv4 Settings” or “IPv6 Settings” tab and select “Manual” as the method.
- In the “DNS” or “Proxy” section, enter the proxy server address and port number provided by your proxy service.
- (Optional) Configure the “Ignore hosts” or “Bypass proxy for these addresses” field to exclude specific websites or domains from using the proxy.
- Click “Save” to apply the proxy settings.
Configuring a Proxy Server on Web Browsers
- Google Chrome:
- Open the Chrome menu and go to “Settings” > “Security and privacy” > “Security and privacy” > “Proxy.”
- Toggle the “Use a proxy server” option to “On” and enter the proxy server details.
- Mozilla Firefox:
- Open the Firefox menu and go to “Settings” > “Network Settings.”
- Select “Manual proxy configuration” and enter the proxy server details.
- Microsoft Edge:
- Open the Edge menu and go to “Settings” > “Privacy, search, and services.”
- Scroll down to the “Security and privacy” section and click “Open proxy settings.”
- Toggle the “Use a proxy server” option to “On” and enter the proxy server details.
- Safari:
- Open the Safari menu and go to “Preferences” > “Advanced.”
- Click the “Change Settings” button next to “Proxies” and enter the proxy server details.
Using a Proxy Server for Anonymous Browsing
While proxy servers can provide a level of anonymity, it’s important to understand their limitations and the potential risks involved. Proxy servers do not offer the same level of privacy and security as a virtual private network (VPN) or the Tor network. To maximize your anonymity when using a proxy server, consider the following best practices:
- Choose a reputable and trustworthy proxy service: Avoid free or low-quality proxy servers, as they may be operated by untrustworthy parties who could potentially log your activities or even compromise your security.
- Enable HTTPS whenever possible: Make sure to use the HTTPS protocol when accessing websites through the proxy server to encrypt your traffic and prevent eavesdropping.
- Combine with other privacy tools: For the highest level of anonymity, consider using a proxy server in conjunction with a VPN or the Tor network, which offers more comprehensive privacy and security features.
- Regularly review and update your proxy settings: Proxy server configurations can change over time, so it’s important to periodically review and update your settings to ensure your privacy and security remain intact.
Troubleshooting Common Proxy Server Issues
- Slow Performance: If you’re experiencing slow browsing speeds when using a proxy server, try switching to a different proxy server or adjusting your browser’s proxy settings
- Connectivity Issues: If you’re unable to connect to the proxy server, check the server address and port number, and ensure that the proxy service is operational.
- Website Accessibility: If certain websites are not accessible through the proxy server, try adding them to the “Bypass proxy server” or “Ignore hosts” list in your proxy settings.
- Authentication Problems: If the proxy server requires authentication, make sure you’re using the correct username and password provided by the proxy service.
- Compatibility Concerns: Some proxy servers may not be compatible with certain browsers or applications. In such cases, you may need to try a different proxy service or use a different method for accessing the internet anonymously.
Conclusion
Proxy servers can be a powerful tool for enhancing your online privacy, security, and accessibility. By understanding the different types of proxy servers and following the step-by-step setup instructions for your operating system and web browser, you can take control of your internet experience and enjoy the benefits of a secure, anonymous, and unrestricted online presence.
Ready to take your online privacy and security to the next level? Sign up for a trusted proxy service today and start browsing the web with confidence. Click here to explore our recommended proxy providers and find the perfect solution for your needs.